Keywords
3D printing,Instrumentation,Microplastics,Mechanical flowmeter,Wastewater-based epidemiologyHow to Cite
(1)
Fabriz Sodré, F.; Rodrigues Augusto, C. E.; de Paula Gonçalves , G. J.; Tavares Schleicher , A.; Fonseca , A. Development and Evaluation of an Electromechanical Flowmeter for Volumetric Flow Measurement: Applications in Wastewater-Based Epidemiology and Microplastic Monitoring in Aquatic Environments. Orbital: Electron. J. Chem. 2025, 17, 289-296.




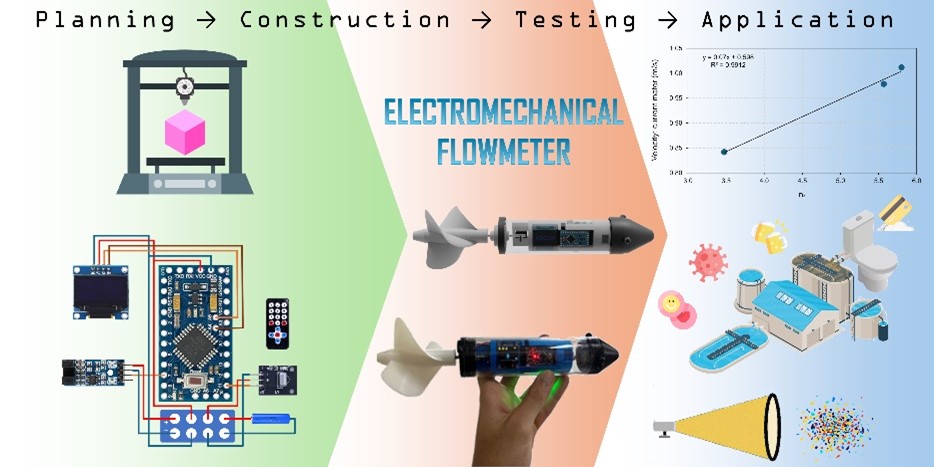
Flow measurement is essential in environmental studies, enabling the calculation of contaminant loads in water and wastewater flows and supporting impact assessments. In wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE), for example, measuring influent flow at wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) is critical for estimating population exposure to drugs and viruses. Mechanical flow meters are also valuable for microplastic studies in aquatic environments, as they measure water volumes passing through plankton nets during sampling. To address the need for reliable and cost-effective flow data, in this study a low-cost electromechanical flowmeter was developed. The device features a compact electronic system based on an Arduino Pro Mini board, sensors, an OLED display, and other components, allowing remote monitoring of rotations, time, and battery autonomy. The structure comprises an acrylic tube, 3D-printed impeller, caps for waterproofing, and supports for electronic circuits. The device demonstrated accurate measurements, was waterproof, compact, and adaptable to various applications. It offers a cost-effective solution, approximately 50 times cheaper than market alternatives, paving the way for innovations in WBE and microplastic research.
Comments (0)